ABSTRACT:
Surgical complications in hair transplant are at times a serious matter. After a follow up for one year post operation, following were the complications: Post operation edema, puriritis, numbness, paraesthesia, bleeding, wide donor scar, sterile folliculitis. Good communication between patient and surgeon, complete clinical and lab assessment of patient, accurate surgical technique trained surgical team are crucial for successful hair transplant with minimal complication rate.
Definition:
Complication is defined as an adverse event that is not considered to be common and which requires change in methodology.
It may be due to surgeon’s planning and technical error or because of patient’s physiology or compliance error.
Surgical Technique:
After ring block in donor area under aseptic condition in patient with stable medical condition.
FUT:
A strip of skin along with hair is cut from the donor area and then the hair is cut into grafts and then the gap in the donor area is stitched by Thchophytic closures.
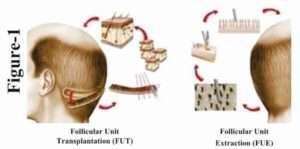
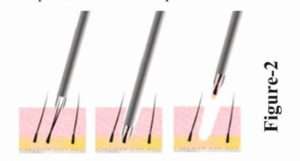
After the graft is extracted it is implanted in the recipient area with the help of needle and forceps.
FUE:
Extraction is done from the safe Donor area with the help of motorised blunt punches or sharp Titanium manual punches.
After the extraction the graft is implanted in the recipient area with the help of needles and forceps or implanter.
Complications and Discussion:
1. Post Operation Oedema: (most common complication)
This occurs on third day of surgery and use of steroid in tapering doses decreases the swelling and inflammation.
Limited use of tumescent anesthesia reduces the chance of post operation oedema. Addition of 1ml adrenaline (1:1000), 2ml Xylocaine -2%, 1ml triamcilone (40mg/ml) in 100 ml. Saline for tumescent anaesthesia
Swelling occurs on the forehead then around eyes and then on the face and is absorbed in a week or 4 to 7 days.
2. Bleeding:(second most common complication)
Stop anabolic steroids, vitamin E, Ginko biloba, Aspirin 10 day prior. NSAID and alcohol – a day prior to decrease risk of bruising and oedema. Vitamin – C per week 2000mg OD BT, CT, PT should be normal and patient should be on Warfarin or Heparin injection.
3. Pruritis:(third most common complication)
This occurs up till 12 week post operation which can be controlled by Antihistamaine as and when required.
4.Numbness Paraesthesia:
Hypoaesthesia, Neuralgia is due to the nerve damage, most commonly in FUT but sometimes Neuralgia is common in diabetic patients undergoing FUE up to 3 – 18 weeks.
5. Wide Donor Scar:
This is common in FUT when the strip is wide and too much of tension is there during closer l/t Hypertrophic scar, keloid.
Mayers Paul scalp, elasticity scale measures the laxity of donors scalp. This scale is guide for estimation of Donor area that can be safely closed with minimum tension.

If a wound closure is in tension, it can lead to necrosis, unpredictable hair loss in donor area and scarring.
In FUE punches ≤ 1 mm should be used and better to punch 1 in every 5th hair and try to cover the entire area even though the number of graft to be extracted is less to avoid moth eaten appearance in the donor area.
6. Sterile Folliculitis: The common cause is in-growing of hair, foreign body reaction epithelium logged into stilt site or piggy backed graft. This is managed by careful insertion of grafts, antibiotics and unrooting of cyst. Sometimes pyogenic granuloma is seen, in such cases. Deroofing of the cyst is a must for complete cure.
Clean and decontaminated operating room, use of sterilized materials, donor area asepsis, disposable instruments, Antibiotics prophylax are vital to prevent infection.
Proper post operation care from patient side is also important for a week or two.
7. Poor Hair Growth: It depends upon the technique of graft desication in FUT.
Rough handling of graft, prolonged out of body time, harmful effects of sterile water, folliculitis, dense placement of graft more than 40-50grafts/sq.cm. Ideal graft placement is 15-25grafts/sq.cm.
Fall of existing hair –DHT created when six reduction converts testosterone to DHT which takes place in blood and locally in the scalp. This DHT acts on genetically susceptible hair follicle to cause miniaturization of hand follicular death.
Koebner phenomenon- d/t surgery trauma. Hair follicle antigen liberated during surgery or post surgery induces hair follicles immune cascade l/t. follicular damage.
Diseased recipient area destroys transplanted hair follicles, so in active Lichen planopilaris, DLE, transplant should be avoided.
8. Cosmetically Unacceptable Result:
Use of large graft and unaesthetic hairline design, failure to anticipate future hair loss in planning, hair line restoration result in unnatural appearance as the patient age increases (large bald areas between lateral aspect of parietal hairline and temporal peak caused by recession of temporal areas).
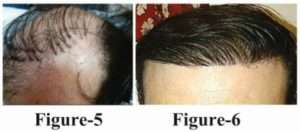
Transplant in crown areas in young individuals result in circular region of transplanted hair surrounded by rim of baldness. When baldness increases as the age advances.
This can be corrected by placement of 1 and 2 hair graft placed in proper direction to create an irregular hairline of gradual increasing density in the center and insert a few grafts beyond the border of the existing hair, so that merging of the hair is done.
Conclusion:
Successful hair transplantation and decreased rate of complication depends on good communication between surgeon and patient, careful clinical and lab evaluation, carefully selected technique, trained surgical team and rigorous post operation evaluation.
References
- Konior RJ. Complication in hair restoration surgery. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2013;21:505-20 [PubMed]
- David PM. Complication in hair restoration surgery. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2009;21:119-48 [PubMed]
- Musgrave R Gradinger G Symposium on Problems and complications in Aesthetic QPlastic Surgery of the faceSt. Lois: Mosby; 1984.pp.3-5
- Lam SM.. Complication in hair restoration surgery. Facial Plast Surg Clin zNorth Am. 2013;21:675-80. [ PubMed]
- Coleman WP.3rd.Kllein JA. Use of the tumescent technique for scalp surgery, dermabrasion and soft tissue reconstruction. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1992;18;130-5.-[ PubMed]
- Unger WP, 3rd ed. Wew York: M Dekkaer:1997